Find the Perfect Music for Your Video: A Data-Driven Workflow (BPM×ASL×Licensing)
Master video music selection with data-driven techniques. Learn BPM matching, ASL calculations, licensing basics & semantic search strategies for perfect soundtracks.

Page Table of Contents
Music in a video could drive emotion, set the pace, and make or break your viewer's experience. Knowing how to efficiently find background music for your content is essential, especially for beginners. This guide shows you a step-by-step process that uses BPM analysis, Average Shot Length (ASL), and smart licensing choices to help you pick music that fits your video's needs.
The 30-Second Workflow: Your Quick Reference
Before diving deep, here's the essential workflow you can reference anytime:
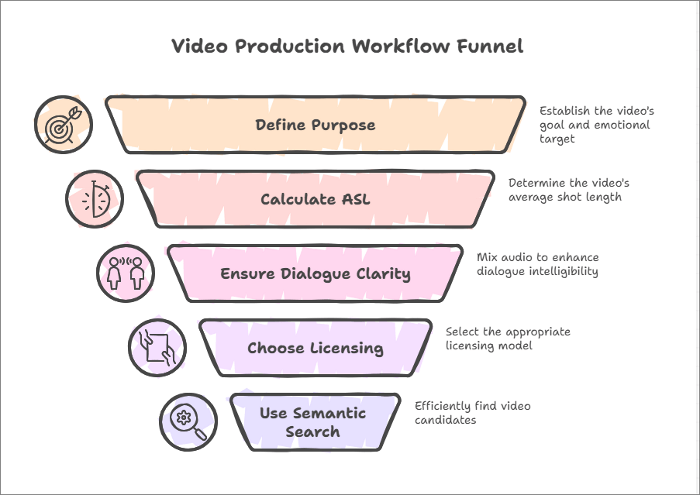
Step 1: Define your video's purpose and target emotion
Step 2: Calculate your video's ASL and match it to the appropriate BPM ranges
Step 3: Ensure dialogue clarity with frequency-aware mixing
Step 4: Choose the right licensing model for your usage
Step 5: Use semantic search techniques to find candidates efficiently
Ready for the detailed breakdown? Let's explore each component.
The biggest mistake novice video creators make is diving straight into music libraries without establishing clear parameters. We can not directly say this is wrong, since you will always and finally find a perfect audio. However, searching them strategically, rather than randomly browsing, saves time and helps you find them quickly.
Define Your Video's Core Purpose
Different video types require fundamentally different musical approaches:
Create Your Mood Lexicon
Develop a specific vocabulary to help you find the perfect BGM. Instead of vague terms like "upbeat" or "calm," use precise descriptors:
Energy levels: Subdued, moderate, energetic, intense, powerful, aggressive, chill...
Emotional qualities: Contemplative, optimistic, urgent, nostalgic, professional, triumphant, melancholic...
Atmospheric elements: Spacious, intimate, dramatic, playful, sophisticated...
Travel /Vlog: adventurous, uplifting, bouncy, joyful, lighthearted, acoustic...
Wedding /Romance: Loving, sentimental. soft, orchestral, romantic...
Comedy / Playful: modern, futuristic, whimsical, goofy...
Scenario-Specific Matrices
Here's how different video types typically align with musical characteristics:
Explainer Videos: Mid-tempo (80-110 BPM), minimal percussion, emphasis on sustained tones
SaaS Demos: Clean production, moderate energy, avoid competing frequencies around 1-3 kHz
Event Recaps: Higher energy (110-130 BPM), dynamic range that matches visual pacing
Documentary-style Brand Films: Cinematic swells, emotional builds that complement narrative arcs
The relationship between your video's visual rhythm and musical tempo isn't guesswork—it's measurable.
Using ASL to Guide BPM Selection
ASL (Average Shot Length) is a simple metric used in film and video analysis to measure pacing. It’s calculated as:
ASL = total scene duration (seconds) ÷ number of cuts
In essence, ASL is a numeric way to describe your video’s visual rhythm.
How ASL connects to BPM (music tempo):
Example: A high-energy fitness montage cut to upbeat pop or percussion-heavy tracks.
Example: A character looking over a cityscape at night underscored by a slow, melancholic piano line.
The power of contrast (breaking the rule):
Sometimes, the strongest choice is to deliberately mismatch music and visuals:
Example: A chaotic battle scene paired with a mournful choir track to highlight the sadness of violence.
Example: A long, quiet shot of someone preparing for a mission with ticking percussion that suggests time running out.
Think of ASL as your video's heartbeat. The music you choose can either sync with that heartbeat—creating harmony and flow—or go against it to produce intentional dissonance. By understanding ASL, you move from randomly picking songs to purposefully scoring your video.
Aligning Song Structure with Video Narrative
Professional music tracks typically follow verse-chorus-bridge structures. Map these to your video's narrative beats:
Verse sections: Ideal for setup, context-building, or detailed explanations
Chorus sections: Perfect for key messages, climactic moments, or calls-to-action
Bridge sections: Useful for transitions, testimonials, or reflective moments
Tools for Precise Audio-Visual Synchronization
Beat Detection: Use software like Adobe Audition's beat detection to identify musical downbeats, then align key visual moments to these markers for maximum impact.
Adobe Remix Tool: This AI-powered feature automatically adjusts song length while preserving musical structure—invaluable when you need a 47-second track but only have a 3-minute song.
Manual Marking: In your video editor, place markers on musical phrases and video beats to experiment with different alignment approaches.
Before worrying about how "good" your music sounds, ensure viewers can clearly understand any spoken content.
The Critical 1-4 kHz Range
Human speech intelligibility depends heavily on frequencies between 1-4 kHz. When selecting music, avoid tracks with prominent elements in this range if dialogue is present. Look for:
Dynamic Ducking Techniques
Some video editing software includes automatic ducking features that lower music levels when dialogue is detected. Adobe Premiere's Essential Sound panel offers one-click presets:
Platform-Specific Audio Standards
Different platforms have varying loudness standards:
YouTube: -14 LUFS integrated loudness
Instagram/TikTok: -16 LUFS integrated loudness
Facebook: -16 LUFS integrated loudness
Broadcast: -23 LUFS integrated loudness
Always check your final mix against these standards to ensure consistent playback across platforms.
Music licensing can be complex, but following a structured decision tree significantly simplifies the process.
Stay Clear of Licensing Pitfalls
Public Domain: No copyright restrictions; ideal for educational videos, historical content, or budget-sensitive projects. Be careful! Recordings themselves may still be protected even if the composition is not.
Creative Commons (CC): Flexible and often free. Check the license type: some require attribution (BY), some prohibit commercial use (BY-NC), and others require “share alike” terms. Free Music Archive (FMA) is a key source.
Royalty-Free Subscription: Platforms like Epidemic Sound or Artlist offer unlimited downloads during your subscription. Cost-effective for YouTubers, streamers, and social media teams.
Commercially Licensed Music: Purchased on a track-by-track basis, typically from libraries such as PremiumBeat, Musicbed, or AudioJungle. Costs more than a subscription but offers broader rights for commercial distribution without the complexity of rights-managed restrictions. A practical middle ground for businesses, agencies, and professionals seeking safe, ready-to-use tracks.
Rights-Managed: Licensed for very specific uses—defined by region, duration, and medium. Often more expensive, but common for advertising campaigns, TV, or film.
Custom Composition: Commissioning original music. Higher cost, but guarantees exclusivity and full compliance. Suitable for major brand campaigns or high-budget productions.

Typical Licensing Scope by Use Case
Geography: Is the license global or limited to certain territories?
Duration: Single campaign for 6 months, or perpetual use?
Media/Channels: Online only, or also broadcast, cinema, events, apps?
Editing & Redistribution: Can the client re-cut or redistribute the video later without re-licensing?
Triple-Check Checklist
Before buying, confirm the license terms (e.g., commercial use allowed, global vs. regional licenses).
Before uploading, check Content ID risks on platforms like YouTube and replace or dispute if flagged.
Before client delivery, ensure usage rights cover the client’s distribution needs (e.g., paid ads, offline events).
🔔Tips:
Always keep license documents. When using CC-licensed tracks (e.g., from Free Music Archive), save both the license screenshot and author credit details—this protects you if disputes arise later.
Just typing a keyword, then previewing one by one? No, stop this. We could do it more systematically.
The Five-Dimension Search Template
Structure your searches using this framework:
Emotion + Instrument + Rhythm + Usage + Negative Terms
Example: "Contemplative piano medium-tempo corporate NOT solo-piano NOT classical"
This approach helps music libraries understand exactly what you're seeking and what to exclude.
Leverage Curated Resources
Rather than starting with massive databases, begin with professionally curated collections:
Platform-Specific Playlists: Services like Epidemic Sound and Soundstripe offer playlists organized by video type, mood, and usage scenario.
Editorial Selections: Look for "Staff Picks" or "Editor's Choice" sections—these typically feature higher-quality, professionally vetted tracks.
Artist Deep-Dives: When you find one track that works, explore the artist's full catalog. Musicians tend to maintain consistent styles that can provide multiple options for ongoing projects.
Recommended Starting Points
Epidemic Sound: Excellent search filters and high production quality. Strong options for ongoing content creation.
Soundstripe: Great value for money with unlimited downloads. Particularly good for YouTube creators.
Envato Elements: Part of a broader creative suite. Useful if you need music alongside other design assets.
YouTube Audio Library: Free option with decent quality. Limited selection but good for budget-conscious projects.
Each platform has unique strengths—Epidemic excels in search functionality, while Soundstripe offers better pricing for high-volume users
Professional Music Supervision Workflow
Understanding how professional music supervisors approach track selection can elevate your own process.
The Brief-to-Mix Process
Creative Brief: Establish mood, reference tracks, and technical requirements before beginning search.
Rights Clearance: Verify licensing early in the process, not after creative decisions are made.
Listening Sessions: Present multiple options with clear rationales for each choice.
Technical Integration: Ensure final selections work within project's audio mixing requirements.
Communication Best Practices
When working with clients or team members:
The music production landscape continues evolving, offering new tools for video creators.
Stems and Component-Based Editing
Many modern music libraries now offer "stems"—individual instrument tracks that comprise a complete song. This allows you to:
Loop Libraries and Modular Construction
Instead of traditional songs, consider building custom soundtracks from loops:
Construction Kits: Collections of complementary loops designed to work together
One-Shot Samples: Individual sounds (drum hits, vocal stings) for punctuation
Ambient Textures: Sustained tones for underlying atmosphere
AI Music and Ethical Considerations
AI-generated music offers new possibilities but requires careful consideration:
Licensing Clarity: Ensure AI-generated tracks include proper usage rights
Platform Policies: Verify that major platforms accept AI-generated content
Attribution Requirements: Understand if and how AI music creation must be disclosed
Quality Standards: AI music quality varies significantly—always preview thoroughly
Essential Workflow Template
Quick Reference Resources
BPM-ASL Compatibility Chart:
| ASL 1-2 sec | 120-140 BPM |
| ASL 2-4 sec | 100-130 BPM |
| ASL 4-8 sec | 80-110 BPM |
| ASL 8+ sec | 60-90 BPM |
Licensing Checklist:
Common Tools & Key Pages (Direct Access Links)
Semantic Search Keywords
Save time with these proven search combinations:
The difference between good and great video content often comes down to music selection. By following this systematic approach, you'll consistently choose music that enhances rather than competes with your message.
Remember that perfect music selection isn't about finding the most beautiful song; it's about finding the track that best serves your video's specific goals and the needs of your target audience. Start with strategy, support with data, and execute with precision.
The tools and techniques outlined in this guide will help you transition from time-consuming trial and error to efficient, results-driven music selection. Your videos—and your audiences—will immediately notice the difference
Discover the top 10 easy piano songs for beginners, including pop, Christmas, jazz, classical, and fun tracks. Learn simple chords, practice tips, and how to play your favorite tunes effortlessly.…

Avoid these common home recording mistakes that ruin your sound. Get professional results with proper mic placement, room treatment, and smart recording habits.…

Learn the 4-step formula to identify any music genre by ear. Master rhythm, instruments, vocals & structure to become a music genre guru fast.…